-
Shapes and features of a human face can possess geometrical proportions which correspond with figures of a heptagon or a pentagon, and also a hexagon, an octagon, a nonagon which are the basic correct equipotent polygons which are necessary for considering during analyses of human faces in physiognomy, or in cosmetic medicine and plastic surgery. As the basic harmonious proportions of a universe are included in the listed polygons.
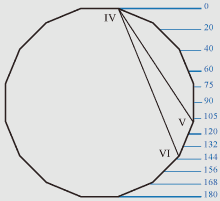
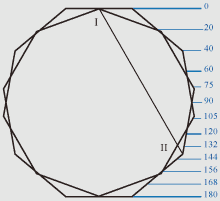
Figure of a hexagon.
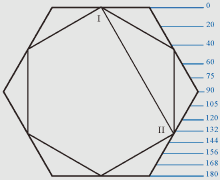
If any lines with designations in the Roman numerals in the shown charts are
parallel for tangent lines to a nose-tip and to the most expressed points of
eyebrows or a forehead, or to lines EI or KI in triangles JKI and JEI then
proportions of a face correspond proportional parities of a hexagon and a
dihexagon (12 angles).
Lines I-II and VII-IX are identical in a hexagon and a dihexagon, and other
lines have different geometrical parameters, but in all cases form the common
complex of harmonious proportions which are uniform for both geometrical
figures.
The information on triangles JKI and JEI look on the previous pages of this
section of website.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of eyebrows is 66 Zn then
proportions of a face correspond proportions of a hexagon, as the line of
eyebrows corresponds with the dihexagonal angle in the point IV.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of a nose is 114 Zn then facial
proportions too correspond proportional ratios of a hexagon, as the line of a
nose corresponds with the dihexagonal angle in the point V.
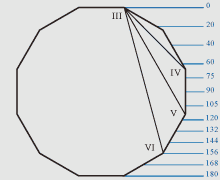
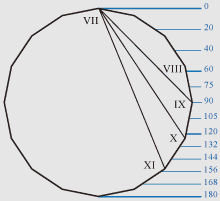
Figure of an octagon.
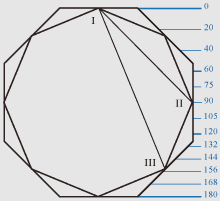
If tangent lines to a nose-tip and to the most expressed points of eyebrows
or a forehead, and also if lines EI or KI in triangles JKI and JEI are parallel
to any lines with designations in the Roman numerals in the shown charts then
proportions of a face correspond proportional parities of an octagon and a
dioctagon (16 angles).
Lines I-II and I-III in octagon are identical to lines VII-IX and VII-XI in
dioctagon, and lines IV-V, IV-VI, VII-X are only in dioctagon. The linear
geometry of two figures forms the common complex of harmonious proportions.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of eyebrows is 55 Zn then facial
proportions correspond proportions of an octagon, as the line of eyebrows
corresponds with the dioctagonal angle in the point VIII.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of a nose is 125 Zn then
proportions of a half face correspond proportional ratios of an octagon, as the
line of a nose corresponds with the dioctagonal angle in the point X.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of a mouth is 141 Zn then
proportional ratios of a face correspond proportions of an octagon, as the line
of a mouth corresponds with the dioctagonal angle in the point VI.
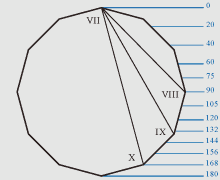
Figure of a nonagon.
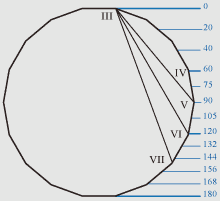
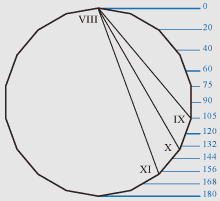
If distance from top of a head up to the line of a mouth is 140 or 149
Zn then proportions of a human face correspond to proportions of a nonagon, as
the line of a mouth corresponds with the nonagonal angle in the point II or with
the angle of a dinonagon (18 angles) in the point VII.
If distance from top of a head up to the line of eyebrows is 60 Zn, and if
distance from top of a head up to the line of a nose is 120 Zn then proportions of
a human face correspond to proportional ratios of a nonagon, as the line of
eyebrows and the line of a nose correspond with dinonagonal angles in points IV и VI.
If tangent lines to a nose-tip and to the most expressed points of eyebrows or a
forehead, and also if lines EI or KI in triangles JKI and JEI are parallel to
any lines with designations in the Roman numerals in the shown charts then
facial proportions correspond proportional ratios of a nonagon.
Pay attention that a dinonagon is a trihexagon, namely the geometrical figure
with 18 angles is variant of a hexagon and a nonagon
Besides it is possible to consider the tangent line to a nose-tip and to the
most expressed point of a chin, which too in a context of physiognomy or from
the point of view of plastic surgery and cosmetology is a parameter of
harmonious proportions of human faces, in the event that this line is parallel
to any lines of correct geometrical figures. For example, the well-known
sculptural image of the ancient Egyptian queen Nefertiti or Neferneferuaten,
or the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten, or the Lady of Grace and
Lady of all Women, or the Beautiful one has come and Beauty of Aten,
if to read different meanings of the Egyptian hieroglyphs.
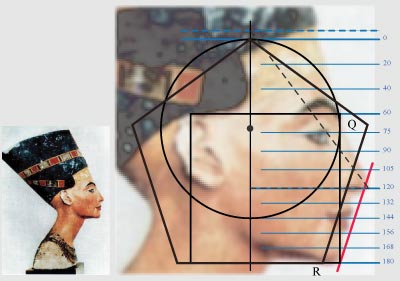 |
The shown facial image of the ancient Egyptian Nefertiti does not allow to see the top line of a head, but the correct sizes of physiognomic spheres of individuality and feelings allow to assume that the size of physiognomic sphere of consciousness is too correct. Namely it is possible to assume that proportions of a face in the sculptural image of Nefertiti have been calculated by ancient Egyptian sculptors according to correct sizes, and consequently each physiognomic sphere has size of 60 zens that allows to find the prospective top line of a head. |
-
Or it is possible to assume that facial proportions in the sculpture of Nefertiti
or the Beauty of Aten correspond to proportions of the sacred Egyptian triangle,
namely triangle JEI specifies top of a head, and then the size of physiognomic
sphere of consciousness presumably should be a little bit more, that is shown on
the chart by a dashed line.
Actually the sphere of consciousness of the Great Egyptian Royal Wife of
Pharaoh Akhenaten had
the much greater size, as on this and other images it is possible to see the
increased skull which is extended upwards, that could be caused by artificial or
even by surgical change of proportions in the childhood, or by genetic anomaly.
Anyhow, but the sizes of physiognomic spheres of individuality and feelings,
and also the prospective correct top line of a head allow to draw the square of
feelings and the circle of consciousness, and allow to compare facial features
to lines of correct geometrical figures that is detailed on the chart is not
shown, but the tangent line to a nose-tip and to the most expressed point of a
chin is shown by red color. This line is parallel to the side of pentagon QR
that specifies one of parameters of harmony in the sculptural facial profile of
the Beautiful one has come as Egyptian Nefertiti or the Lady of all Women.
Other parameters of harmony in the half-face of Nefertiti in particular are:
- correct lines of eyebrows and a nose - 60 and 120 zens;
- concurrence of the ear to lines of eyebrows and nose;
- correct line of a mouth, and concurrence of this line to size of the circle of
consciousness - 144 zens;
- concurrence of the upper eyelid with the line of top of nose bridge - 75 zens.
And also sculptural image of Nefertiti has some other proportional ratios which
determine harmony of facial features.
Except for the basic geometrical figures such as a pentagon, a heptagon, a
hexagon, an octagon, a nonagon, it is possible to compare features
of human faces to lines of figures with 11, 13, 17 angles. Total there are 14 correct equipotent
polygonal figures
which determine geometrical parameters of harmony in faces of people. In aggregate
polygons form natural system which is shown on the chart.
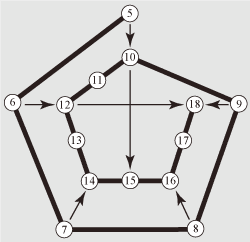 |
The quantity of angles in polygons is shown by
numbers, namely numbers in circles from 5 up to 18 symbolize the
appropriate polygons. For example, the circle with number 6 symbolizes a
hexagon and the circle with number 8 symbolizes an octagon. The dark spiral line designates sequence in which polygons are located according to increase in quantity of angles. The external spiral convolution contains the basic geometrical figures: a pentagon, a hexagon, a heptagon, an octagon, a nonagon. The internal spiral convolution contains variants of the basic geometrical figures: a dipentagon, a dihexagon, a diheptagon, a tripentagon, a dioctagon, a dinonagon. And also the internal spiral convolution contains minor geometrical figures with 11, 13, 17 angles. Interrelations of the basic geometrical figures with variants are shown by arrows. |
The basic figures in the external spiral convolution have the greatest value,
and figures in the internal spiral convolution have smaller value. Namely if any
features of a human face are similar to lines of the basic geometrical figures
then such similarity are most appreciable. But figures of the internal spiral
convolution too have values. For example, if there are concurrences to shapes of
a dinonagon then it strengthens impressions caused by concurrences of facial
features to shapes of a hexagon or a nonagon, but deforms impressions caused by
concurrences to octagonal forms.
Geometrical figures can be coordinated or not coordinated, and accordingly
individual proportions in faces of people can be harmonious or disharmonious,
that matters in physiognomy, and also in plastic surgery and cosmetic medicine.
If facial features are similar to shapes of any one geometrical figure and to
variants of this figure then individual proportions of a face are harmonious.
But if facial features are similar to different geometrical figures and to
variants of different figures then individual proportions can be harmonious or
disharmonious.
Hexagon and nonagon, and also variants with 12 and18 angles are coordinated to
each other.
Hexagon and octagon, and also variants with 12 and 16 angles are coordinated.
Heptagon and nonagon, and also variants with 14 and 18 angles are coordinated.
Hexagon and heptagon, and also variants with 12 and 14 angles are not
coordinated to each other.
Heptagon and octagon, and also variants with 14 and 16 angles are not
coordinated.
Octagon and nonagon, and also variants with 16 and 18 angles are not
coordinated.
Pentagon and also variants with 10 and15 angles are coordinated to shapes of any geometrical figures.
In essence, coordination of polygons can be
considered as interrelations of five elements in the Chinese numerology, namely five
basic geometrical figures can be compared to five elements of the Chinese numerology, and
accordingly it is possible to consider coordination of figures as interaction of
elements, that is shown on the chart.
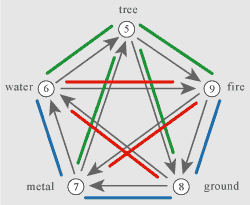 |
Five elements (tree - water -
metal - ground - fire) are located as a five-pointed star. Grey arrows
show interrelations of elements in a context of Chinese
numerology. Numbers from 5 up to 9 in white circles symbolize the appropriate polygons which are correlated to elements of Chinese numerology. It is necessary to take into account that numbers in circles mean quantity of angles in polygons, and are not symbols of numerological numbers. The information on numbers of the Chinese numerology and the information on interrelations of five elements look on pages of this website in other section with the name: half faces (concepts 2). Blue lines specify the not coordinated combinations of polygons, and red lines specify the coordinated combinations. Green lines specify that shapes of a pentagon are coordinated to any geometrical figures. |
Ratios of five basic geometrical figures and their variants to shapes of
polygons with 11, 13, 17 angles form more complex natural system which is shown
on following page in this section of website. These ratios are perceived as
harmonious or disharmonious distortions of the basic figures. But if in facial
features there are shapes of any one figure then a face seems harmonious. For
example, if features of a human face are similar to shapes of a polygon with 11
angles then there are harmonious proportions. But if in facial features there
are similarity to other geometrical figures then shapes of a polygon with 11
angles can be perceived as harmonious or disharmonious distortion.
The shown ratios of geometrical figures are caused by complex numerical
numerological laws. These laws are essential and necessary for understanding of
beauty in view of physiognomy, and also in a context of cosmetic medicine and
plastic surgery. Namely medical cosmeticians and plastic surgeons should analyze
faces of people and find similarity to shapes of geometrical figures, then it is
possible to do conclusions about harmonious or disharmonious facial proportions.
Each human face is individual also has unique formal features which distinguish
one person from another, that demand individual research of geometrical laws.
Such physiognomic researches can be necessary in cosmetology or in plastic
surgery when it is necessary to calculate the necessary changes of facial shapes
which are required for achievement of correct result of plastic operation or
cosmetic procedure.
In the end of this page I bring to your attention the diagram of facial angles
which can be used during physiognomic calculations, and also this diagram can be
used by plastic surgeons and cosmeticians.

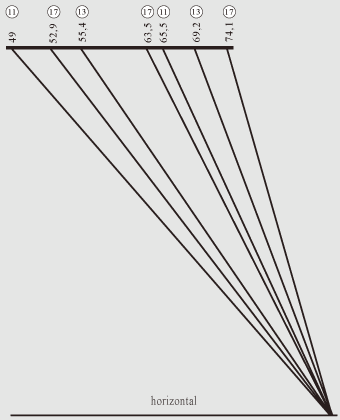
The main line of the diagram is the horizontal which is parallel to CD side
in the square
of feelings.
The information on the square of feelings look on 2nd page of this website
section.
The slanting lines correspond to shapes of correct equipotent polygons. Above near to
each slanting line there are sizes of angles to the main horizontal, and also
numbers from 5 up to 18 in circles specify the appropriate polygons to which
slanting lines correspond.
Comparison of slanting lines with features of a human face allows to see
similarity of facial features to shapes of geometrical figures.
For physiognomic analyses, and also for researches of human faces in cosmetic
medicine and plastic surgery it is possible to correlate the shown diagram of
facial angles to photos of people in graphic computer programs. Or it is
possible to develop the special computer program for plastic surgeons and
cosmeticians who correct shapes of noses or lips, namely perform rhinoplasty or
nose job, or other facial operations,
and change proportions in faces of people. If cosmetic clinics and hospitals or
medical centers of plastic surgery are interested in such computer software.
The following page results the information on psychological features which are caused by concurrences of facial features to shapes of geometrical figures, and also gives the information on subjective perception of harmonic proportions and beauty in human faces.
-