       Page 8. |
 |
The eighth page compares rings of hexagrams of the Book of Changes i-jing with physiognomic symbols of analytical psychology in four rings which correspond to quarters of a magic square. |
-
Also rings of hexagrams of the Book of Changes i-jing can be compared with physiognomic symbols of psychological types in analytical psychology according to ratio of physiognomic symbols with hexagrams and quarters of a magic square, that is shown in the table:
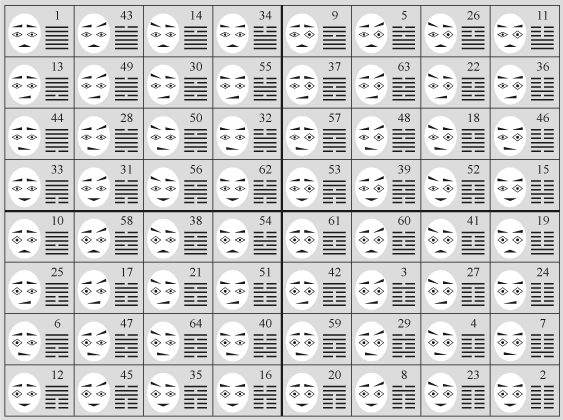 |
Physiognomic symbols of 64 psychological types
correspond with hexagrams i-jing according to digrams which are double
combinations of lines in hexagrams. Top digrams correspond to eyebrows, middle digrams correspond to eyes, bottom digrams correspond to a mouth. At each quarter of a magic square in the shown table there are physiognomic symbols with identical parameters of eyes as hexagrams i-jing have identical middle digrams in each quarter, and consequently it is possible to correlate physiognomic symbols of psychological types of analytical psychology to rings of hexagrams. |
In the first ring parameters of eyes correspond to digrams which consist
of two entire lines.
In the second ring parameters of eyes correspond to digrams which consist
of the bottom entire line and the top break line.
In the third ring parameters of eyes correspond to digrams which consist
of the bottom break line and the top entire line.
In the fourth ring parameters of eyes correspond to digrams which consist
of two break lines.
At the level of eyes:
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious introversion;
- digram corresponds to
obvious introversion;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active extraversion;
- digram corresponds to
active extraversion;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active introversion;
- digram corresponds to
active introversion;
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious extraversion.
- digram corresponds to
obvious extraversion.
At the level of eyebrows:
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious logics;
- digram corresponds to
obvious logics;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active ethics;
- digram corresponds to
active ethics;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active logics;
- digram corresponds to
active logics;
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious ethics.
- digram corresponds to
obvious ethics.
At the level of a mouth:
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious intuition;
- digram corresponds to
obvious intuition;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active sensory;
- digram corresponds to
active sensory;
![]() - digram corresponds to
active intuition;
- digram corresponds to
active intuition;
![]() - digram corresponds to
obvious sensory.
- digram corresponds to
obvious sensory.
According to the listed parameters it is possible to identify psychological
types of analytical psychology, and it is possible to analyze parities of types
in rings of hexagrams i-jing.
The detailed information on psychological
types of analytical psychology look in other section of this website.
-
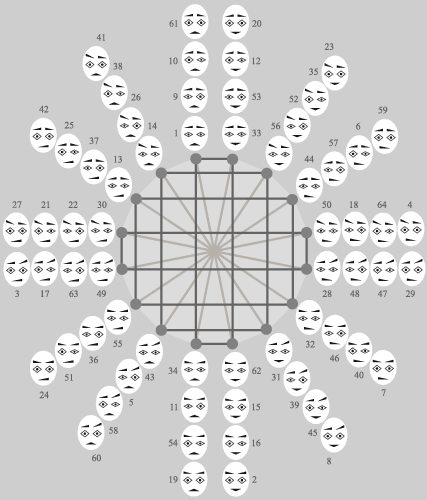 |
In the first ring psychological types have
parameters of obvious introversion. In the second ring - parameters of active extraversion. In the third ring - parameters of active introversion. In the fourth ring - parameters of obvious extraversion. For example, 28th psychological type in the first ring possesses obvious introversion, and 47th psychological type in the third ring possesses active introversion. Dark and grey lines designate parities of psychological types within four rings. Namely it is possible to see that psychological types have identical eyebrows concerning dark lines on horizontals, and have identical mouths concerning dark lines on verticals. And psychological types have opposite physiognomic parameters of eyebrows and mouths concerning grey lines. According to the shown scheme it is possible to analyze interrelations of psychological types, and also it is possible to analyze many other laws of analytical psychology. |
The following page shows parities of hexagrams of the Book of Changes i-jing in rings with functional types of analytical psychology, and also speaks about interrelations of psychological types.
-